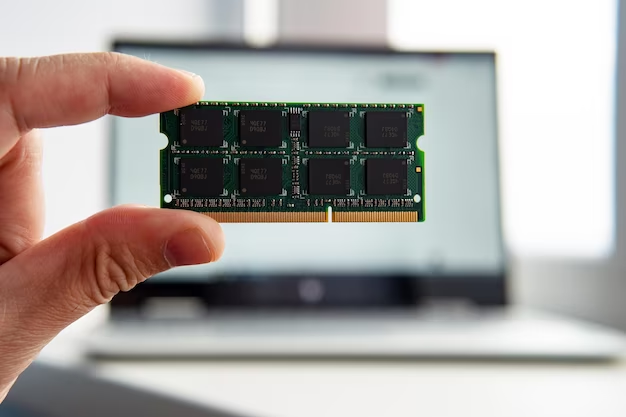
Understanding RAM Slots in Laptops: A Deep Dive
The modern world thrives on technology, and one of the most essential components of our digital devices is RAM (Random Access Memory). This dynamic memory module plays a crucial role in the performance of laptops, allowing them to run multiple applications simultaneously and handle complex tasks with ease. However, have you ever wondered how RAM is integrated into laptops and how these memory modules are connected? Enter the realm of RAM slots in laptops, a topic that holds the key to understanding the memory hierarchy and overall system performance. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of RAM slots, exploring their significance, types, installation process, and frequently asked questions.
The Significance of RAM Slots
RAM slots serve as docking points for the memory modules in laptops. These slots allow users to expand the memory capacity of their laptops, enhancing their overall performance. RAM, often referred to as the “working memory,” is used by the laptop’s operating system and applications to store data that is actively being used or processed. The more RAM a laptop has, the more data it can keep readily accessible, resulting in smoother multitasking, faster application launches, and improved overall responsiveness.
Understanding RAM Slots
Envision your laptop as a grand theater, with the CPU as the visionary director, the storage drive as the vast script repository, and the RAM as the stage upon which the drama unfolds. RAM, commonly referred to as Random Access Memory, takes on the role of the actors, breathing life into data for the CPU’s manipulation. However, this theater can accommodate only a limited ensemble of actors at any given time. Enter the RAM slots – the seating area for these actors between their performances.
Table: A Theatrical Analogy
| Component | Theatrical Equivalent |
|---|---|
| CPU | Director orchestrating the performance |
| Storage Drive | Repository of scripts |
| RAM | Actors bringing scripts to life |
| RAM Slots | Seating for actors between scenes |
RAM’s Crucial Role
Imagine your laptop’s operating system and applications as different acts within a larger performance. When you juggle multiple applications or browser tabs, you’re essentially staging a complex multitasking spectacle. Each act demands swift data processing, and RAM serves as the backstage storage, facilitating seamless transitions between scenes. With greater RAM capacity, your laptop becomes a spacious backstage area, accommodating numerous performers and ensuring a smooth, uninterrupted performance.
Table: Multitasking Metaphor
| Scenario | Metaphor |
|---|---|
| Multitasking with limited RAM | Crowded stage with cramped actors |
| Multitasking with ample RAM | Spacious stage with room for diverse performances |
| RAM expansion via slots | Expanding the stage for an even grander show |
Unveiling RAM’s Potential
Picture this: Your laptop’s performance space resembles a tightly packed venue. Here’s where the brilliance of RAM slots comes into play. These unassuming slots offer the opportunity to expand your laptop’s backstage area, accommodating more actors and enabling grander performances. By introducing additional RAM modules into these slots, you’re essentially amplifying the available workspace for data processing. This empowerment equips your laptop to effortlessly handle resource-intensive tasks without missing a beat.
Speed and Responsiveness
Visualize your laptop’s tasks as intricate puzzles. The CPU functions as the master solver, relying on pieces from the puzzle to maintain a swift tempo. RAM slots function as nimble couriers, delivering these puzzle pieces to the CPU with lightning speed. Increased RAM capacity allows these couriers to transport larger bundles of data, resulting in swift application launches, seamless video editing, and an overall heightened user experience.
Embracing the Future
In an era of rapid technological advancement and ever-evolving software demands, the significance of accessible RAM slots cannot be overstated. Upgrading your laptop’s RAM is akin to investing in future tasks and applications. Furthermore, it offers a cost-effective method of revitalizing an aging laptop, extending its usefulness and ensuring its relevance in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Types of RAM Slots
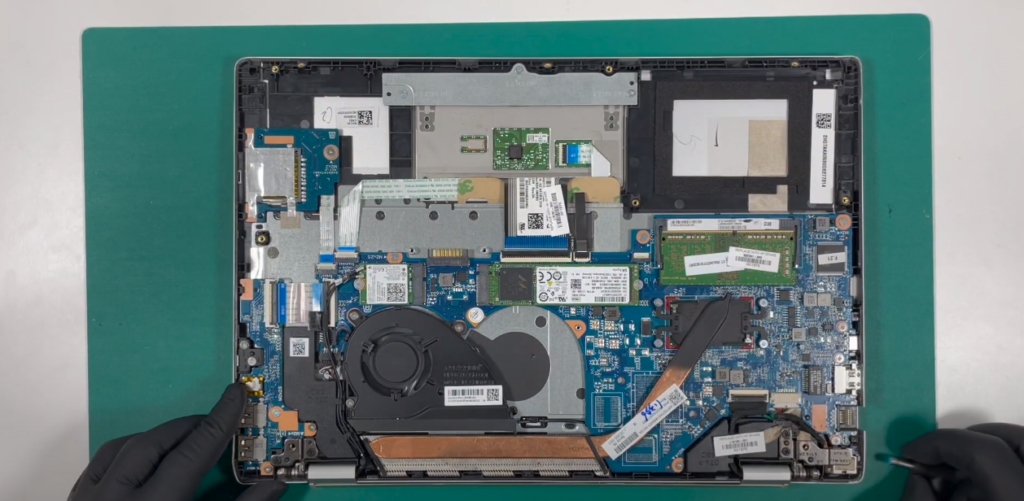
Imagine a bustling cityscape, where each district serves a distinct purpose. Just as the city’s neighborhoods cater to different lifestyles, laptops offer varied RAM slot options to cater to specific needs. Two primary RAM slot types reign supreme: SODIMM (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module) and DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module). These slots are like gateways, welcoming different kinds of memory modules into the laptop’s core.
SODIMM Slots
Picture a SODIMM slot as a cozy nook in a bustling metropolis – compact yet efficient. These slots have earned their place in the hearts of laptops due to their small size and optimal efficiency. They are the embodiment of space-saving innovation, tailor-made for laptops’ slender frames. Just as a city accommodates diverse communities, SODIMM slots come in various generations, with DDR4 and DDR3 being the most prevalent.
Table: SODIMM Slots – Compact Powerhouses
| Slot Type | Attributes | Common Generations |
|---|---|---|
| SODIMM | Compact and efficient | DDR4, DDR3 |
| DIMM | Larger size, desktop prevalence | DDR4, DDR3 |
DIMM Slots
Now, shift your gaze to the magnificent architecture of DIMM slots – the towering pillars of desktop computing. Just as grand skyscrapers dominate city skylines, DIMM slots command attention with their larger size and distinct presence. Unlike their compact SODIMM counterparts, DIMM slots are more commonly found in desktop computers. They offer a spacious haven for memory modules, accommodating greater capacity and potentially boosting overall performance.
Generations of SODIMM
In the chronicles of technological advancement, memory modules evolve through generations, each representing a leap forward in efficiency and capability. DDR4 and DDR3 are the champions of the SODIMM world, capturing the essence of progress. These generations define the standards by which data is processed, allowing laptops to adapt to the ever-shifting demands of contemporary computing.
Table: Generations of SODIMM Slots
| Generation | Advancements and Features |
|---|---|
| DDR4 | Higher data transfer rates, improved efficiency |
| DDR3 | Significant upgrade over DDR2, enhanced capacity |
The Symphony of Laptop Performance: RAM Slot Harmony
Imagine a symphony where diverse instruments harmonize to create captivating melodies. Similarly, RAM slots collaborate with memory modules to compose the laptop’s performance symphony. SODIMM and DIMM slots, each with their unique characteristics, cater to laptops and desktops respectively, ensuring an optimized and seamless experience tailored to the device’s form and function.
Installation Process
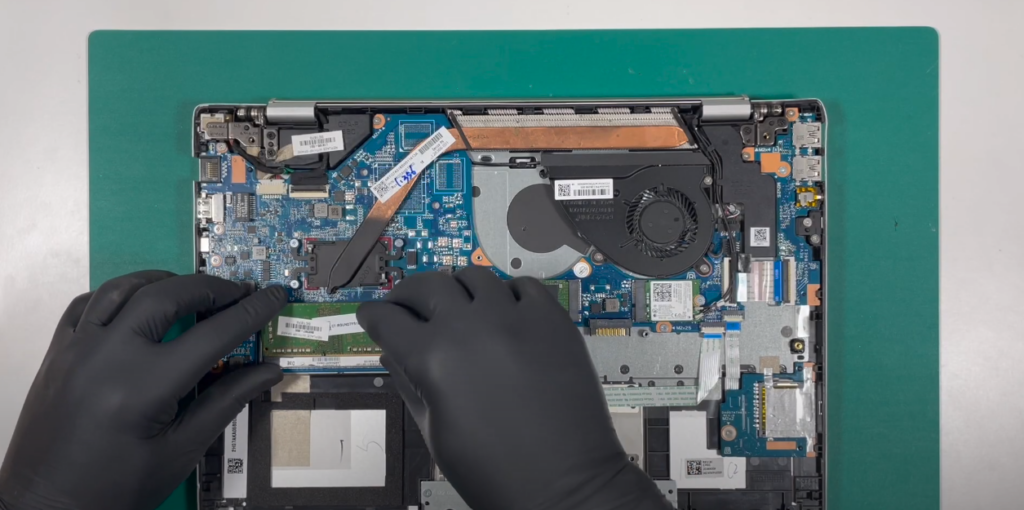

Adding more RAM to a laptop can be a relatively simple process, provided you have the compatible memory module and the necessary tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to installing RAM in a laptop:
- Check Compatibility: It’s essential to ensure that the RAM module you’re purchasing is compatible with your laptop’s specifications, including the type (DDR3, DDR4, etc.), speed, and capacity;
- Gather Tools: You’ll need a small Phillips-head screwdriver and an antistatic wrist strap to prevent electrostatic discharge that could damage the sensitive components;
- Power Down: Turn off your laptop and disconnect it from any power source. This ensures your safety and prevents potential damage during the installation process;
- Locate the RAM Slots: Most laptops have access panels on the underside that can be removed to reveal the internal components, including the RAM slots. Consult your laptop’s user manual to find the exact location;
- Ground Yourself: Wear an antistatic wrist strap to discharge any static electricity and prevent damage to the laptop’s components;
- Remove Existing RAM (If Necessary): If you’re replacing existing RAM modules, gently press the retaining clips on the sides of the module in an outward direction. The module should pop up at an angle, allowing you to remove it;
- Insert the New RAM: Align the notches on the RAM module with the slot, ensuring proper orientation. Gently press down on the module until the retaining clips click into place on both sides;
- Close Up: If you removed an access panel, secure it back in place. Reconnect the laptop to its power source;
- Power On: Turn on your laptop and check if the new RAM is recognized. You can verify this in the system settings or use third-party software.
Conclusion
In the world of laptop performance, RAM slots play a pivotal role. These unassuming components enable us to enhance our laptops’ capabilities and make them more adept at handling modern computing tasks. Understanding how RAM slots function and how to upgrade them empowers users to optimize their laptops’ performance and productivity. For a more visual guide on this topic, check out this link to a video that demonstrates the installation process step by step:
So, next time you find your laptop lagging behind, consider diving into the world of RAM slots to give it the boost it deserves.
FAQ
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a dynamic memory module that plays a vital role in a laptop’s performance. It functions as the laptop’s “working memory,” allowing the operating system and applications to store and access data that is actively being used or processed. This enables smoother multitasking, faster application launches, and improved overall responsiveness.
RAM slots in laptops serve as docking points for memory modules. These slots enable users to expand their laptop’s memory capacity, leading to enhanced performance. Adding more RAM to your laptop provides more space for data that can be readily accessed, resulting in improved multitasking capabilities and faster data processing.
In most cases, you can upgrade the RAM in your laptop to improve its performance. However, it’s important to ensure compatibility with your laptop’s specifications, including the type (DDR3, DDR4, etc.), speed, and capacity. Refer to your laptop’s user manual or manufacturer’s website to find information about compatible RAM modules and installation instructions.
SODIMM (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module) and DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) are two primary types of RAM slots found in laptops and desktops, respectively. SODIMM slots are compact and efficient, designed for laptops’ slender frames. They accommodate smaller memory modules, such as DDR4 and DDR3. DIMM slots, on the other hand, are larger and commonly found in desktop computers. They can accommodate larger memory modules and have DDR4 and DDR3 variants.